Introduction to LCD Technology
LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) is one of the most widely used display technologies today, powering everything from smartphones and televisions to industrial control panels and digital signage. Unlike traditional CRT (Cathode Ray Tube) displays, which use electron beams to create images, LCDs rely on a backlight and liquid crystals to control light passage and generate images. This technology has revolutionized the way we experience digital content, providing brighter, clearer, and more energy-efficient displays.
How LCD Displays Work: The Basics
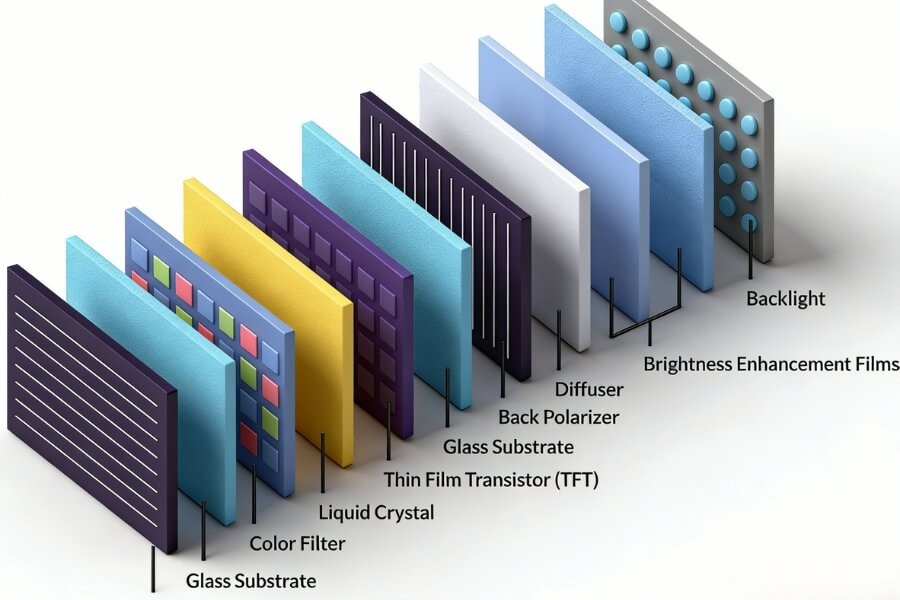
At the core of LCD technology lies the principle of controlling light passage. LCDs don't emit light themselves; instead, they manipulate light that passes through them. The technology works like an optical valve, adjusting how much light gets through based on the alignment of liquid crystal molecules.
- Liquid Crystal Layer: The liquid crystal material in LCDs can twist or align when an electric field is applied. These molecules control the light passing through the screen, either blocking or allowing it based on their alignment.
- Polarizing Filters: Two layers of polarizing filters are used to manage the light's direction. The light passes through the first filter, and the liquid crystal layer adjusts its orientation. If the molecules are aligned correctly, light passes through the second polarizer, creating a visible image.
- Backlight: Since LCDs do not emit light by themselves, they require a backlight, which is typically either LED or CCFL (Cold Cathode Fluorescent Lamps). The backlight illuminates the screen and provides the light that the liquid crystals either block or allow to pass.
Choosing the Right LCD Panel for Your Business
Understanding the different types of LCD panels available is essential when choosing the right display for your needs. Below are some common LCD panel types and their ideal use cases:
TN Panels (Twisted Nematic)
- Pros: Quick response times, lower cost.
- Cons: Limited color accuracy and narrow viewing angles.
- Ideal For: Dynamic content displays like gaming advertisements, where fast response time is prioritized over color quality.
IPS Panels (In-Plane Switching)
- Pros: Superior color accuracy, wider viewing angles (nearly 180°), better contrast.
- Cons: Slower response times compared to TN panels.
- Ideal For: High-end retail displays and design previews, where color precision and wide viewing angles are essential.
VA Panels (Vertical Alignment)
- Pros: High contrast ratio, deep blacks.
- Cons: Slower response times, narrow viewing angles.
- Ideal For: Immersive experiences such as video walls or cinematic ads where contrast and black levels are prioritized.
LTPS Panels (Low-Temperature Poly-Silicon)
- Pros: High resolution, low power consumption.
- Cons: Expensive to produce.
- Ideal For: Small mobile display applications, like interactive screens and portable devices.
The Key Benefits of LCD Technology in Commercial Displays
LCD technology offers several advantages that make it ideal for a variety of commercial display applications:
- Energy Efficiency: Compared to older technologies like plasma and CRT, LCDs consume significantly less power, making them perfect for long-running commercial applications.
- Long Lifespan: LCD displays typically last over 100,000 hours, making them reliable and cost-effective over time.
- No Burn-in: Unlike OLED, which may suffer from burn-in when static images are displayed for too long, LCDs do not suffer from this issue, making them ideal for static content like menus and information screens.
- High Resolution and Large-Scale Integration: LCDs support high-resolution content and can be used in video walls, large-scale digital signage, and other high-impact commercial applications.
- Customization Options: LCD displays can be customized with touch capabilities, anti-glare coatings, high brightness, and outdoor protection features.
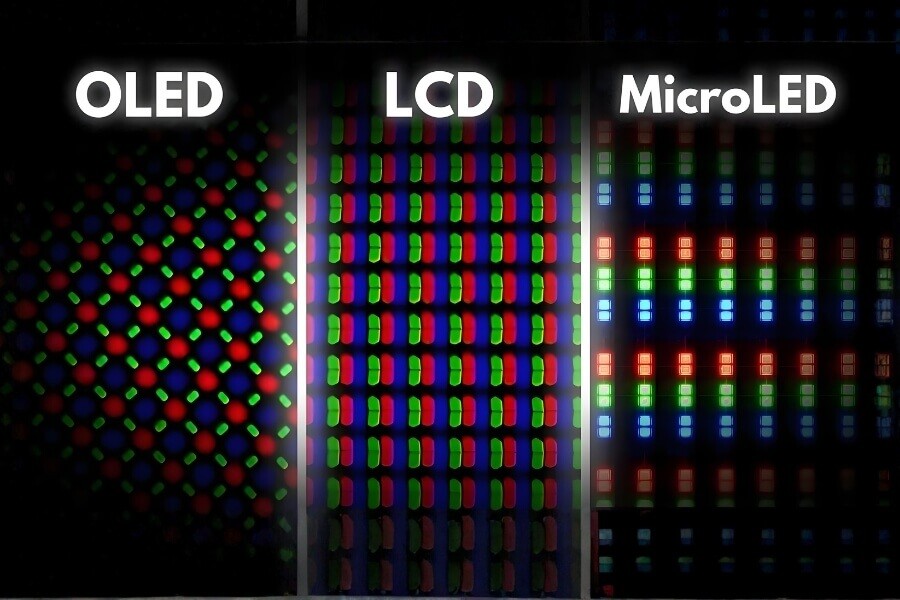
LCD vs OLED vs MicroLED: A Commercial Display Selection Guide
When choosing between LCD, OLED, and MicroLED for commercial displays, each technology has distinct features. Here’s a quick comparison:
| Feature | LCD (Commercial) | OLED (Premium Display) | MicroLED (Emerging) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brightness | High (supports HDR) | Medium to High | Extremely High |
| Contrast | High (VA panel best) | Extremely High (self-emissive) | Extremely High |
| Viewing Angles | Wide (IPS) | Extremely Wide | Extremely Wide |
| Power Consumption | Low (best for static content) | Low (black content saves energy) | Medium |
| Lifespan | Long (replaceable backlight) | Short (organic materials degrade) | Expected to be long |
| Cost | Low (mature industry) | High | Extremely High |
| Best Use Cases | Digital signage, video walls, info displays | High-end retail, exhibition, transparent displays | Large stage, virtual production |
RUSINDISPLAY Perspective:
In our Transparent OLED Display Systems, we combine the stability of LCD with the visual impact of OLED, making it perfect for high-end applications like storefront windows, interactive exhibition displays, and immersive spaces.
LCD for Large-Scale Displays: Best Practices for Video Walls and Digital Signage
For large-scale commercial displays, such as video walls and digital signage, the technology’s ability to handle high-definition content, deliver crisp images, and support seamless integration makes LCD an ideal choice.
- Seamless Integration: Our systems support bezel-less, narrow-edge installations, ensuring smooth, uninterrupted visuals across large video walls.
- High Refresh Rate & Low Latency: Perfect for dynamic advertising and live broadcasts, where responsiveness and real-time interaction are key.
- Smart Brightness Adjustment: Adaptive brightness based on ambient light levels, ensuring optimal viewing in various lighting conditions while saving energy.
RUSINDISPLAY Perspective:
We provide Turnkey Video Wall Solutions, offering end-to-end services from hardware integration, content management, to interactive features. Our solutions are already being used in shopping malls, exhibition centers, and corporate image walls.
Looking Ahead: The Integration of AI with Display Technology
The future of display technology lies in its integration with AI, which will significantly enhance the functionality of commercial displays.
- AI-Driven Content Adaptation: Real-time content personalization based on audience profiles and behavior.
- Enhanced Visual Interactivity: Combining cameras and sensors to enable face recognition, gesture controls, and more.
- Smart Energy Efficiency: AI algorithms will optimize brightness and refresh rates to extend device lifespan and reduce power consumption.
RUSINDISPLAY Perspective:
We are developing AI-powered Transparent OLED Interactive Systems that can identify user behavior and trigger relevant content. This technology is ideal for smart retail, exhibition interactivity, and branded experience spaces.
FAQ
Q1: What’s the difference between an LCD and LED display?
An LED display uses LED backlighting with an LCD panel. True LED displays (like OLED or MicroLED) use self-emissive pixels that offer more vibrant colors and better contrast.
Q2: How do I choose the right LCD panel for commercial display?
For retail displays, choose IPS for accurate color and wide viewing angles. For dynamic advertising, VA panels provide higher contrast. For interactive applications, opt for IPS with touch functionality.
Q3: What maintenance is required for LCD video walls?
To maintain LCD video walls, regularly clean the screens, ensure proper ventilation, avoid static images, and use surge protectors to prevent power spikes.
Q4: How does transparent OLED differ from traditional LCD in display applications?
Transparent OLED displays offer a “floating visual” effect, ideal for window displays and interactive setups. LCDs, on the other hand, excel in high-brightness and clarity for static content like information screens.




