1. Moving Beyond Screens: The Rise of Spatial UI and Transparent OLED
The Limitations of Traditional Displays
Traditional displays are confined to flat screens, limiting the interaction dimensions and trapping content within a fixed frame. The digital world has always been restricted to screens, forcing users to engage in a two-dimensional world that cannot fully capture the depth and complexity of real-life interactions.
The Rise of Spatial Computing
With the advent of Augmented Reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR), Mixed Reality (MR), and transparent display technology, interfaces are moving from the 2D realm into 3D spaces. These innovations open up new ways for users to engage with the digital world, offering immersive experiences where the boundaries of screens disappear.
The Role of Transparent OLED
Transparent OLED technology is crucial in enabling this transition. By allowing digital content to seamlessly integrate with the physical environment, transparent OLED creates a truly interactive experience, where digital and physical worlds coexist naturally. This allows businesses to display dynamic content without losing the connection to the real world.
RUSINDISPLAY's Position
As a leading provider of high-end transparent OLED display solutions, RUSINDISPLAY is at the forefront of pushing spatial interaction into real-world applications, focusing on commercial displays, retail advertising, and other dynamic environments.
2. Understanding Spatial UI: A New Way to Interact with the Digital World
Spatial UI refers to the design and presentation of user interfaces in 3D spaces. Unlike traditional interfaces that rely on flat screens, Spatial UI enables users to interact with digital elements in their physical surroundings. With natural methods like gestures, eye movements, and voice commands, users can engage with the interface in a more intuitive and immersive way.
Core Features of Spatial UI
- No Screen Dependency: Content no longer resides on a flat screen. Instead, it exists in the real world, allowing users to interact with it from multiple angles and perspectives.
- Diverse Input Methods: Spatial UI uses gesture recognition, eye-tracking, and voice commands, making interactions feel more natural.
- Depth Perception & Spatial Memory: Spatial UI enhances user engagement by adding a layer of depth and context to interactions, enabling better memory retention and comprehension.
- Multi-Tasking & Dynamic Layouts: Spatial UI supports multiple tasks simultaneously, with content arranged in a dynamic 3D space for easier access and organization.
- Collaboration with Transparent OLED: Transparent OLED serves as the display medium for Spatial UI, allowing digital content to float and blend seamlessly into the physical environment.
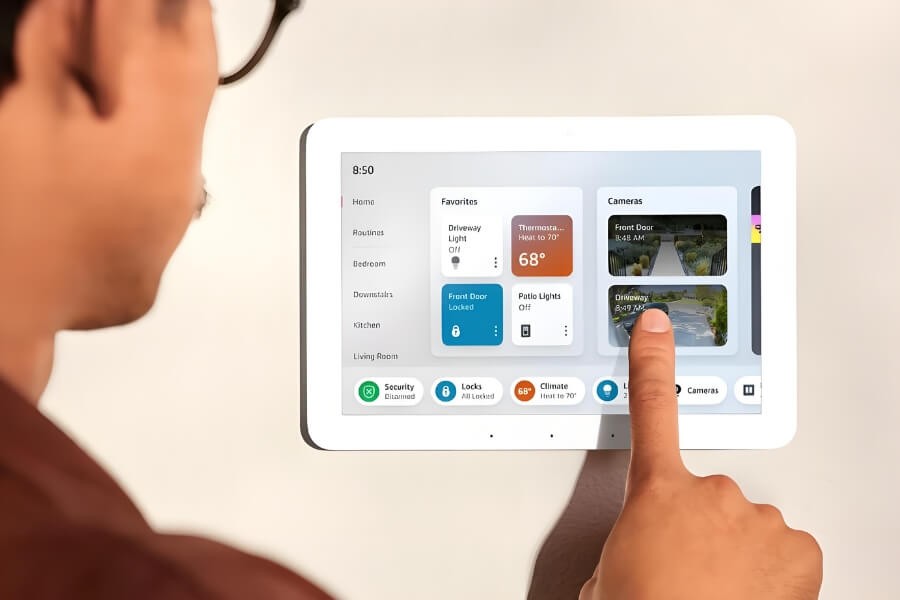
3. Why Transparent OLED Matters in Spatial UI Design
Technology Principles
Transparent OLED displays use organic light-emitting materials combined with transparent electrodes. Unlike traditional displays, these screens emit their own light without the need for backlighting, enabling transparency levels of 35%-45%. This design allows ambient light to pass through, maintaining visibility of the physical world while displaying digital content.
- Self-Emissive Technology: No backlight is needed, making the display thinner and more flexible.
- Transparency: Users can see through the display, maintaining a connection to the environment.
- High Contrast & Clarity: Transparent OLED provides excellent clarity and contrast even in thin, frameless configurations, enhancing the user experience.
- High-Performance Visuals: The display offers vibrant colors and sharp contrast, ensuring high-quality visuals even in low-light environments.
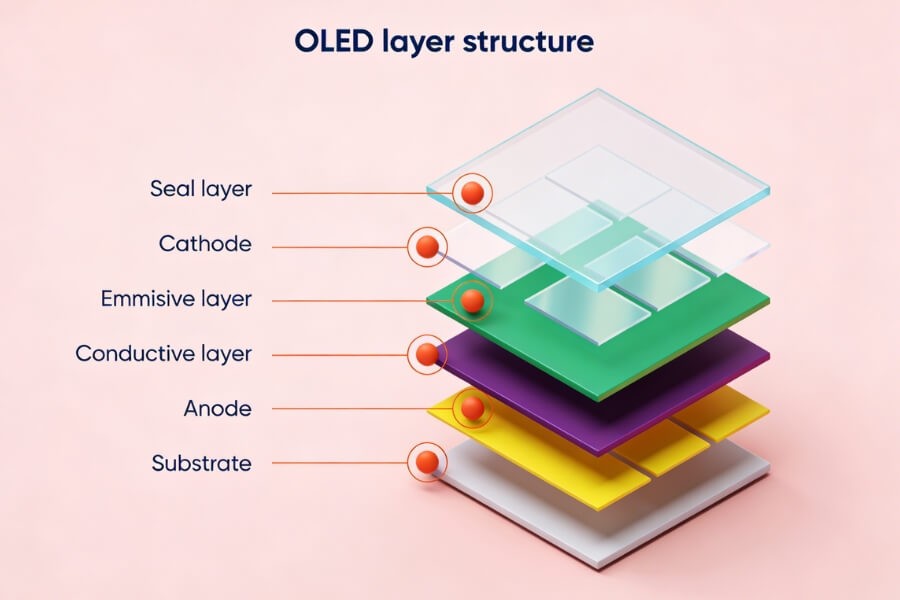
Core Advantages
- High Transparency: Ideal for environments like shop windows, exhibition halls, and command rooms, where maintaining visibility of the real world is essential while showcasing digital content.
- Thin and Flexible: Transparent OLED displays can be seamlessly embedded into glass, walls, or curved surfaces, making them adaptable to various architectural designs.
- Visual Performance: Offers stunning color vibrancy and high contrast, ensuring that digital content grabs attention and enhances the visual experience.
RUSINDISPLAY's Offerings
- Transparent OLED Display Series: Our display solutions come in various sizes and transparency levels to meet different business needs.
- Modular Video Wall Systems: Customizable resolutions and shapes, perfect for large-scale display installations.
- Integrated Interactive Technologies: Our displays come with built-in touch, gesture recognition, and AI-powered content responses to create engaging, dynamic experiences.
4. Designing for Space: How Transparent OLED Enhances Spatial UI
View and Comfort Design
To enhance comfort, it's important to position primary content within the center of the user’s field of view. Secondary information should be placed at the edges, ensuring it is accessible without causing unnecessary neck or body movement. This ensures that the user can engage with the content naturally without physical strain.
Spatial Layering & Depth Management
- Z-Axis Use: Utilize the Z-axis to create foreground, midground, and background depth, adding a sense of spatial organization to the design.
- Layered Content Display: Transparent OLED allows for content to be displayed in layers, creating a more immersive experience where digital elements appear to float within the physical space.
Natural Interaction & Feedback Design
Transparent OLED displays support intuitive interactions, such as hand gestures, eye movements, and voice controls. Coupled with spatial audio and haptic feedback, these interactions enhance immersion, making users feel as though they are engaging with real objects in their environment.
Environmental Adaptation & Content Persistence
Transparent OLED content adapts to changes in environmental lighting and space size. The technology also supports "object persistence," where virtual content stays anchored in its physical location, even when the display is powered off or restarted.
5. Transforming Industries: Transparent OLED in Retail, Ads, and More
High-End Retail and Window Displays
Example: Luxury stores use transparent OLED video walls to overlay dynamic brand stories and product details, enhancing visual appeal and increasing customer engagement.
RUSINDISPLAY’s Solution: Custom transparent display systems + interactive content for touch queries and AI recommendations.
Digital Billboards & Public Space Interactions
Example: Transparent OLED billboards at airports displaying live flight information alongside advertisements, ensuring visibility and non-intrusive content layering.
Technical Highlight: High brightness for outdoor settings and remote content management.
Exhibition Displays and Museum Experiences
Example: Transparent OLED screens are placed behind artifacts, showcasing restoration animations and educational content.
RUSINDISPLAY’s Service: Creative content + hardware integration for end-to-end display solutions.
Control Rooms and Data Visualization
Example: Transparent OLED panels embedded in command room glass walls, enabling real-time data overlay while maintaining visibility of the physical space.
Technical Requirements: High refresh rates, low latency, and multi-signal input support.
6. The Future of Displays: AI, Interactivity, and Transparent OLED
AI-Powered Content Generation & Personalized Displays
Transparent OLED systems will integrate AI to dynamically adjust content based on user behavior, such as age, gender, and engagement time. This allows for real-time personalization and smarter user experiences.
Multi-Modal Interaction Enhancement
The future of interaction is multi-modal. Transparent OLED displays will support gestures, eye movements, voice commands, and touch, allowing for greater flexibility and adaptability to user preferences.
Ongoing Display Technology Evolution
- Higher Transparency: Transparent OLED will evolve with higher transparency levels, improved flexibility, and lower power consumption.
- MicroLED Integration: Combined with transparent OLED for better brightness and durability, creating even more powerful visual experiences.
RUSINDISPLAY’s Future Plans
- AI + Transparent OLED: Developing smart advertising systems with AI integration for dynamic content display.
- Expansion into Immersive Spaces: Modular transparent video walls and curved OLED displays for immersive environments.

7. Getting Started with Transparent OLED: A Guide to Implementing Spatial UI
Requirements Analysis & Scenario Definition
- Project Goals: Define whether the goal is brand presentation, interactive advertising, or data monitoring.
- Environment Evaluation: Consider lighting, space size, viewing distance, and installation methods.
Hardware Selection & System Integration
- Display Selection: Choose the right transparent OLED size, transparency, and resolution.
- Integration: Incorporate touch, sensors, and content control systems.
Content Design & Interaction Development
- Layered Content: Design content layers that balance environmental integration and information delivery.
- Natural Interaction Logic: Develop intuitive gestures and voice control systems to avoid user fatigue.
Testing & Optimization
- Real-World Testing: Test visibility, interaction smoothness, and system stability in real-world environments.
- User Feedback: Adjust content layout and interaction design based on user feedback.
8. FAQ
Q1: Can Transparent OLED Be Used in Strong Light?
Yes, new transparent OLED displays feature high brightness and anti-reflective coatings, making them suitable for both indoor and outdoor environments, ensuring clear visibility in various lighting conditions.
Q2: Does Spatial UI Require AR/VR Devices?
No, transparent OLED displays can create spatial interaction effects on their own, without requiring AR/VR devices, allowing users to experience immersive content with just the display.
Q3: Is the Maintenance Cost of Transparent OLED Video Walls High?
Transparent OLED video walls are low-maintenance due to the absence of backlighting, offering long lifespan and energy efficiency. Modular replacement options keep costs manageable and ensure easy upkeep.
Q4: How Should Content Be Designed for Transparent OLED?
Content should be layered, with key information displayed in opaque areas while background elements remain transparent to ensure environmental visibility and enhance user interaction.
Q5: Which Industries Can Benefit from Spatial UI?
Industries like retail, advertising, exhibitions, museums, and command control can benefit from Spatial UI, where visual impact, environmental integration, and interactive experiences are essential.
Q6: What is Spatial UI?
Spatial UI is a design approach where digital content is integrated into 3D space, allowing users to interact with it using natural inputs like gestures, eye movement, and voice commands.
Q7: What is a Spatial Interface?
A spatial interface allows users to engage with digital content in a 3D environment, enabling interaction through natural movements, enhancing immersion and accessibility in virtual or mixed environments.
Q8: What Are the 4 Types of UI?
The four main types of UI are Graphical User Interface (GUI), Voice User Interface (VUI), Touch User Interface (TUI), and Gesture-Based User Interface (GBUI), each designed for different user interaction methods.
Q9: What is an Example of a Spatial UI in a Game?
In VR games, spatial UI enables players to interact with in-game elements by moving their hands, eyes, or body. For example, players can grab items or open menus by gesturing in the game space.




